What Molecule Does a Sequence of Dna Typically Code for
Usually the insert is the interesting part consequently. What does the sequence of bases in a DNA molecule represent or what does DNA code for.
The sequence tells scientists the kind of genetic information that is carried in a particular DNA segment.

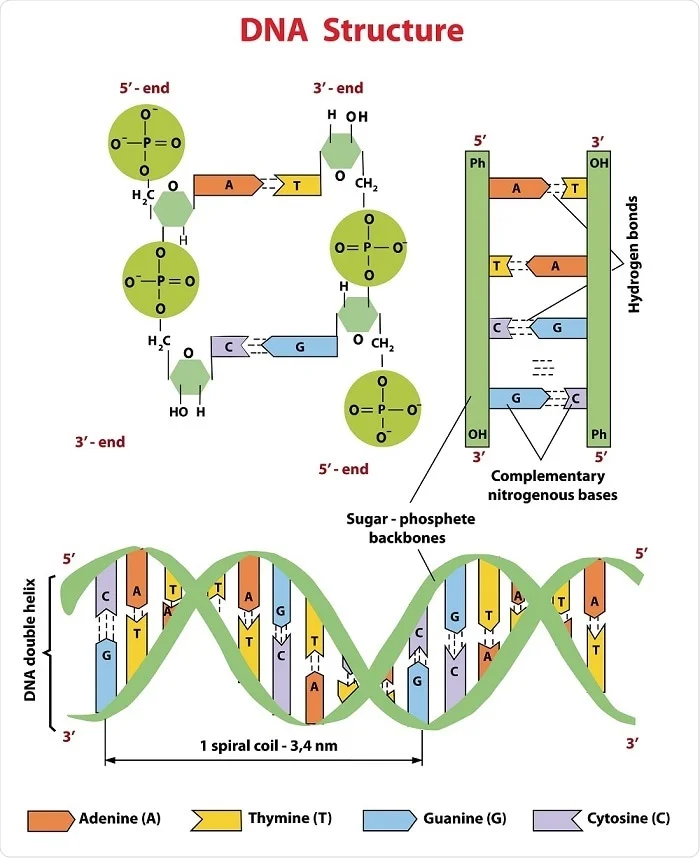
. It consists of a specific sequence of nucleotides at a given position on a given chromosome that codes for a specific protein or in some cases an RNA molecule. April 09 2016 021101 AM. What building blocks form a DNA molecule.
Both of these codons code for proline. What sequence of events occurs in the process of protein synthesis. A fever in a normally healthy adult during an illness is not usually a.
How does DNA in cells determine an organisms complex traits. Additionally what is the importance of the sequence of nucleotides in genetic information. The coding strand is the DNA strand that has the same sequence DNA ATTGC would be RNA AUUGC as the mRNA transcript.
What molecule does a sequence of DNA typically code for. Sequencing DNA means determining the order of the four chemical building blocks - called bases - that make up the DNA molecule. DNA sequence act as a blue print for protein synthesis.
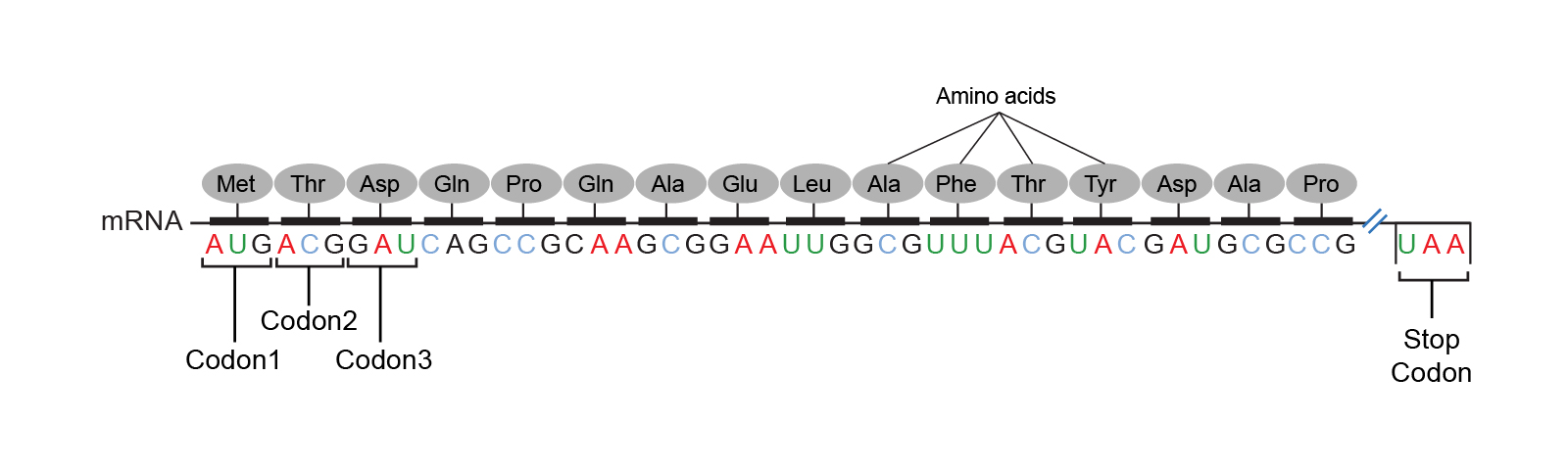
The translated sequence is AUA-AAG-AGC ILA- LYS-SER. The DNA nucleotides codes for codons on an mRNA strand in transcription the codons will then pair with a tRNA molecule that holds an amino acid. Adenine A thymine T cytosine C and guanine G.
What molecule does a sequence of DNA typically code for. The side rails are composed of units called nucleotides which are made of two substances. Click here to get an answer to your question What does the sequence of bases in a DNA molecule represent or what does DNA code for.
DNA is a molecule not a code. Coding regions called exons which specify a sequence of amino acids. Itll direct the ribosomal machinery of the cell about which amino acid should be incorporated into the growing peptide chain in order to get desired protein.
There is no source no receiver no probability space no unique mapping and most of all no letters or alphabets in DNA. The first line of the input file contains the number of species and the number of sites. The information of a particular protein is coded by nucleotide triplets within the gene known as codons.
What would happen to the final product produced from your DNA sequence if the first C in your sequence was. Coding regions called exons which specify a sequence of amino acids. Where does the sequence of bases that is found within your DNA come from.
The vector is generally the basic type of DNA molecule used to replicate your DNA like a plasmid or a BAC. Answer 1 of 4. The gene that codes for a particular polypeptide includes the base sequence shownGAGTACCCTWhat is the base sequence of the mRNA molecule which is complementary to this sequence.
What structures in the nucleus of the cell is DNA found. If you narrowly consider a mathematical definition of code then DNA is obviously not a code any more than gravity is. Imagine that a mutation in a DNA molecule results in the codon CCU being changed to CCC.
A phosphate group and a sugar. It consists of a specific sequence of nucleotides at a given position on a given chromosome that codes for a specific protein or in some cases an RNA molecule. Sequencing DNA means determining the order of the four chemical building blocks - called bases - that make up the DNA molecule.
This nucleotide series represents the whole genetic information of the organism. The amino acids will then form a chain in the sequence of the DNA nucleotide sequence. Upgrade to remove ads.
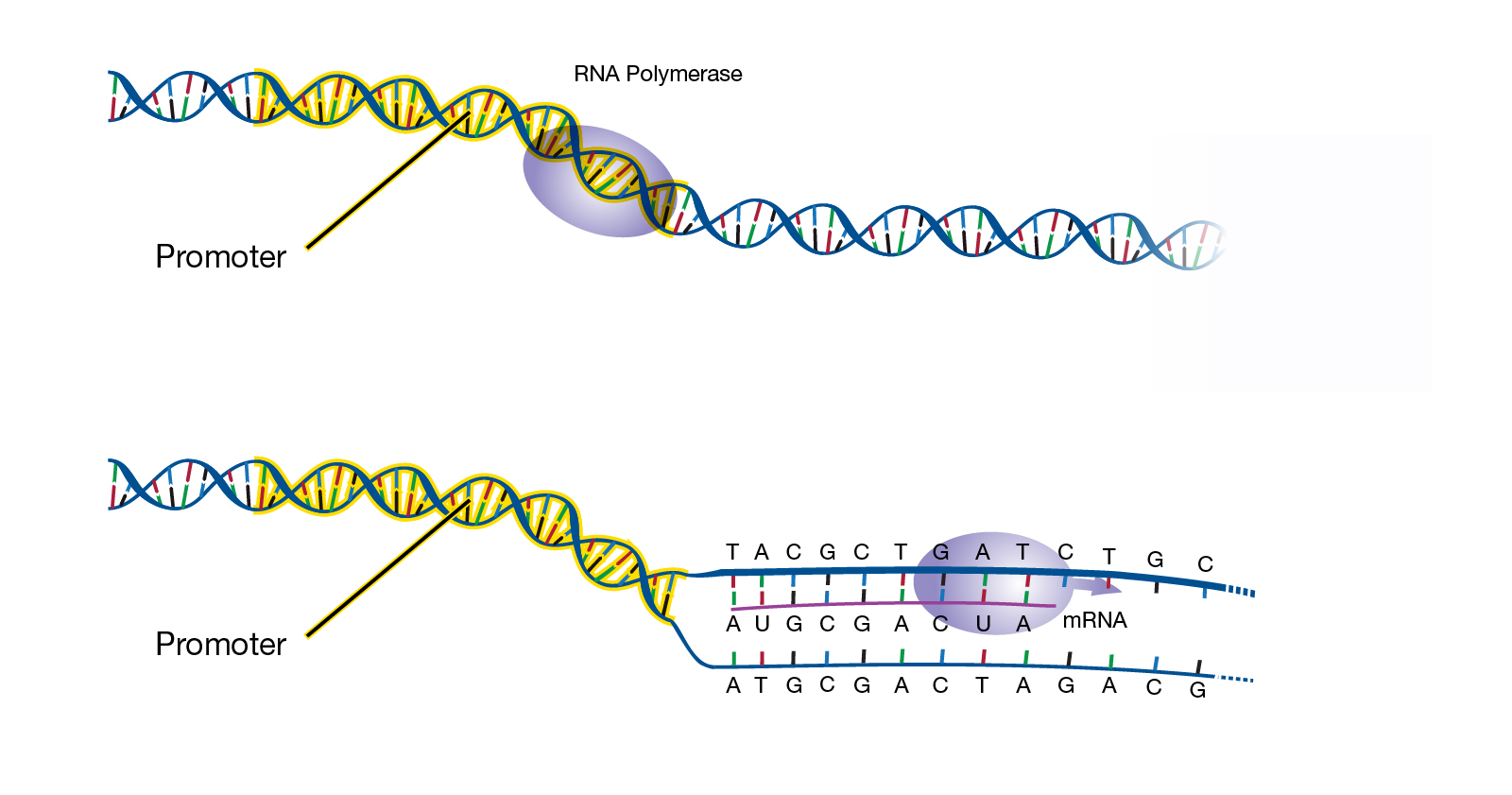
Insert The insert is a piece of DNA weve purposely put into another a vector so that we can replicate it. The input format for the DNA sequence programs is standard. Transcription occurs--mRNA travels to ribosome---translation occurs--- amino acids link to form proteins.
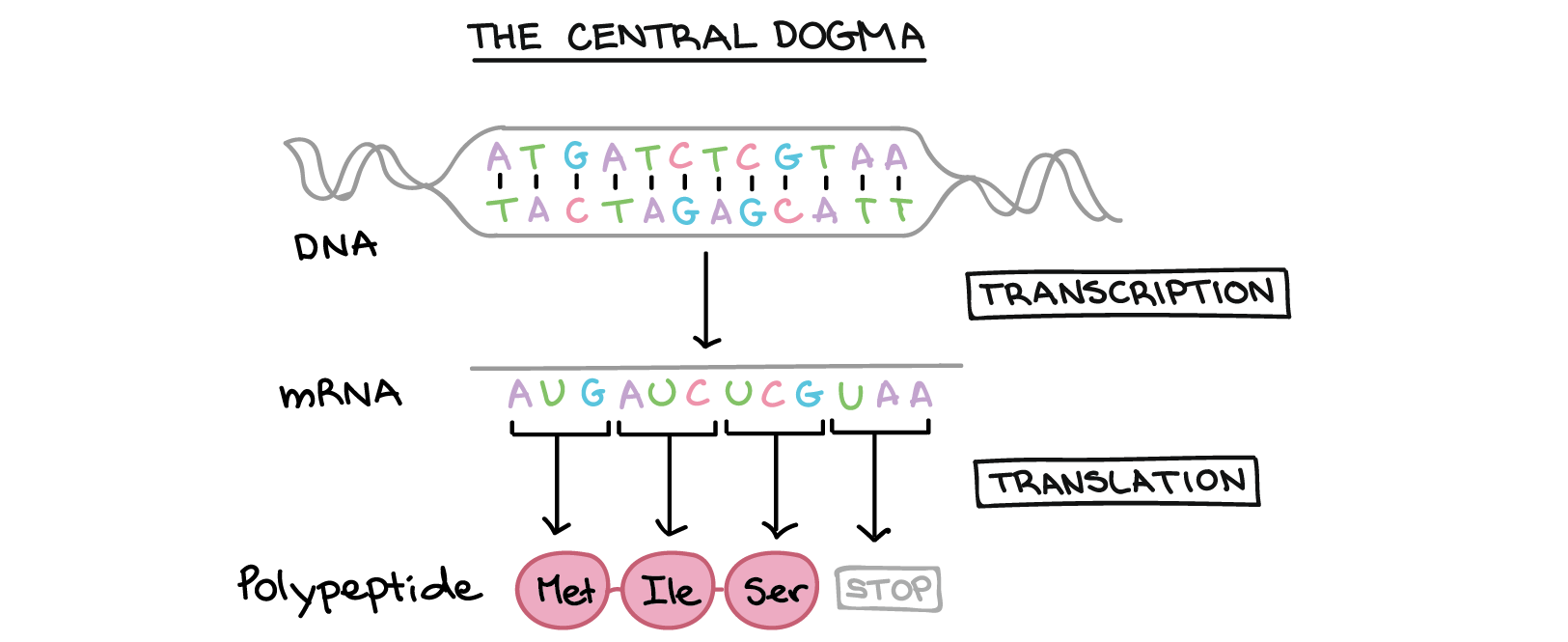
This should enable you to use output from many multiple-sequence alignment programs with only minimal editing. DNA RNA protein. What sequence best describes the process of protein sythesis.
INPUT FOR THE DNA SEQUENCE PROGRAMS. Josejulian1202 josejulian1202 11012019 Biology Middle School answered What does the sequence of bases in a DNA molecule represent or what does DNA code for. In a genome genes are NOT arranged so that there is a single template strand - for some transcripts the top strand is the template and for others its the bottom strand FYI these strands have nomenclature too and the template and coding.
What amino acid sequence would result from this DNA. The data have As Gs Cs and Ts or Us. Genes consist of three types of nucleotide sequence.
The protein coding regions within the nucleotide series are known as genes. B the redundancy of the genetic code. A DNA contains codes for proteins which are necessary for the growth and functioning of an organism.
Which of these DNA strands will code for the amino acid sequence glycine-serine-glycine. Its a freaking molecule not an abstract concept. The rungs of a DNA molecule stand for small chemical bases.
The ordersequence is important as. This phrasing is a little confusing because a. What molecule does a sequence of DNA typically code for.
Which molecule remains in the nucleus during protein synthesis. A DNA molecule is made up of a series of nucleotides. The sequence of nucleotides in a DNA molecule determines the protein that will be produced.
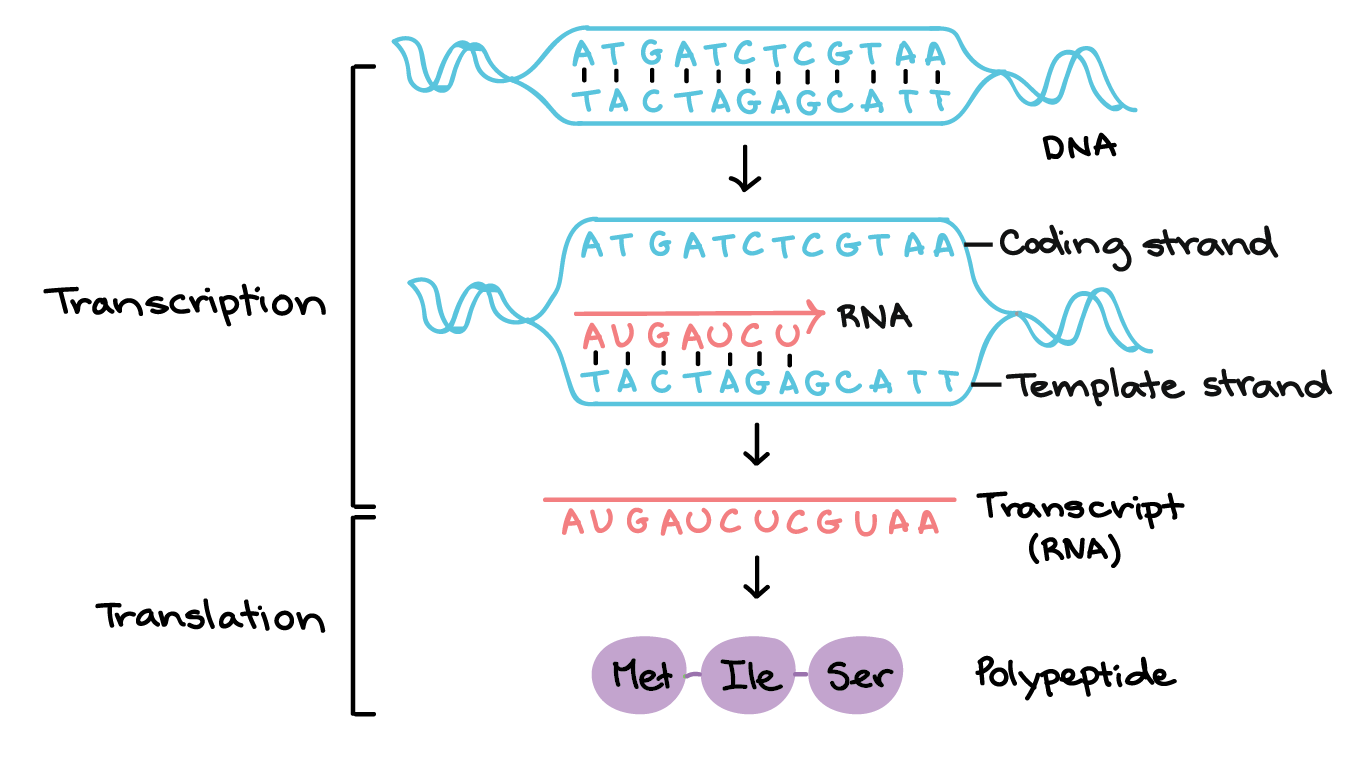
Stages Of Transcription Initiation Elongation Termination Article Khan Academy

Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks
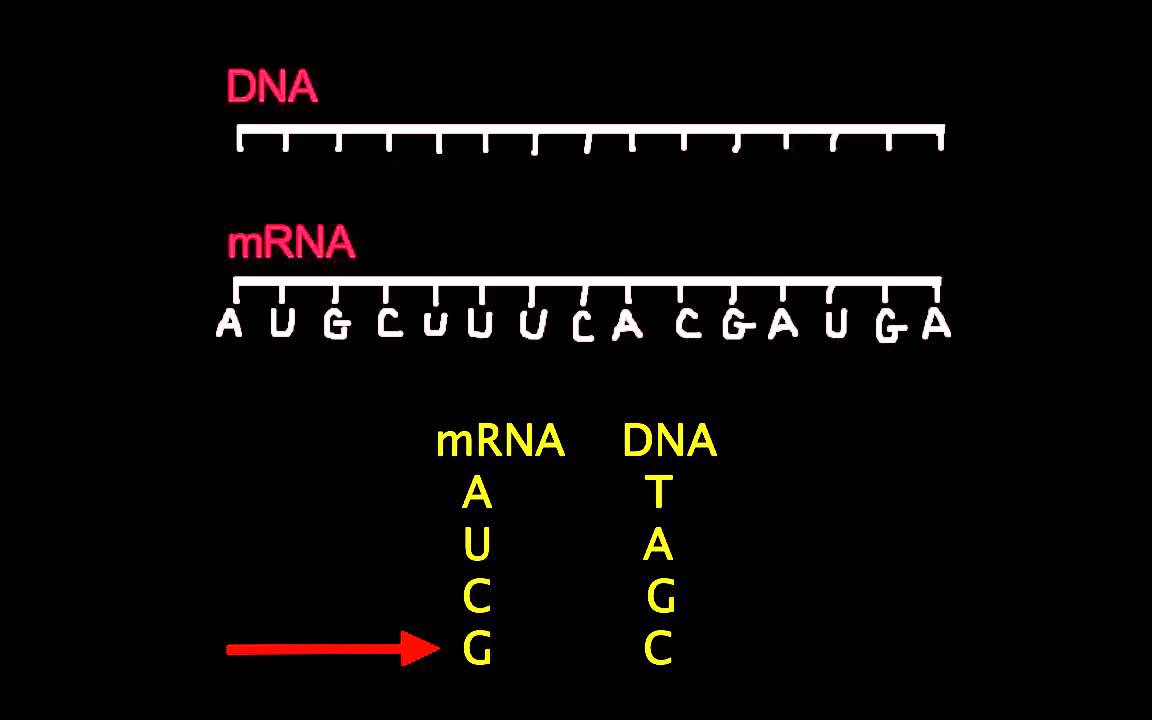
Topic 2 7 Dna Replication Transcription And Translation Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green
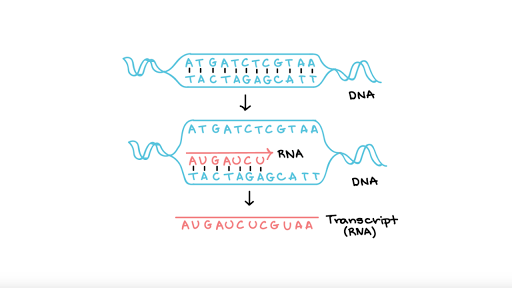
Transcription An Overview Of Dna Transcription Article Khan Academy
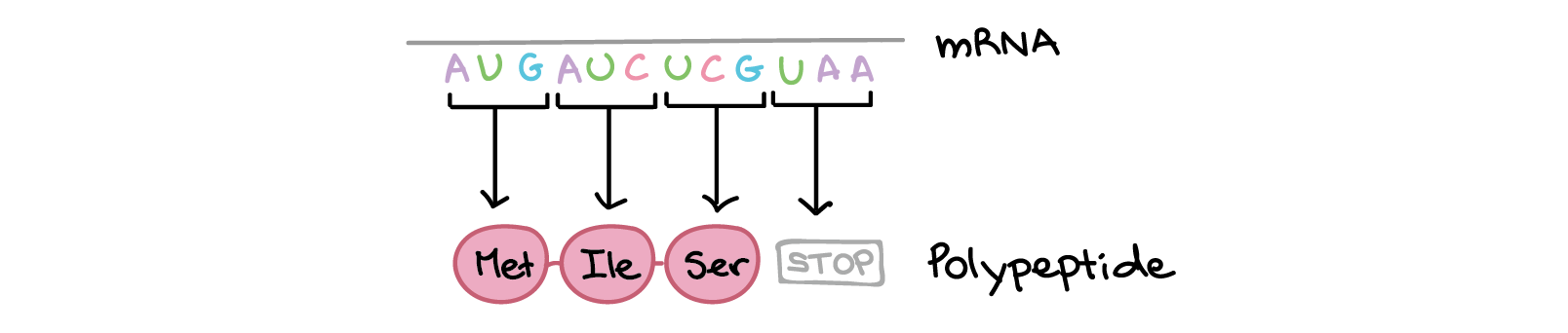
Intro To Gene Expression Central Dogma Article Khan Academy

Repeated Sequence Dna An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Dna Coding And Codons What Is A Dna Codon Ancestrydna Learning Hub

Life Dna Rna And Protein Britannica
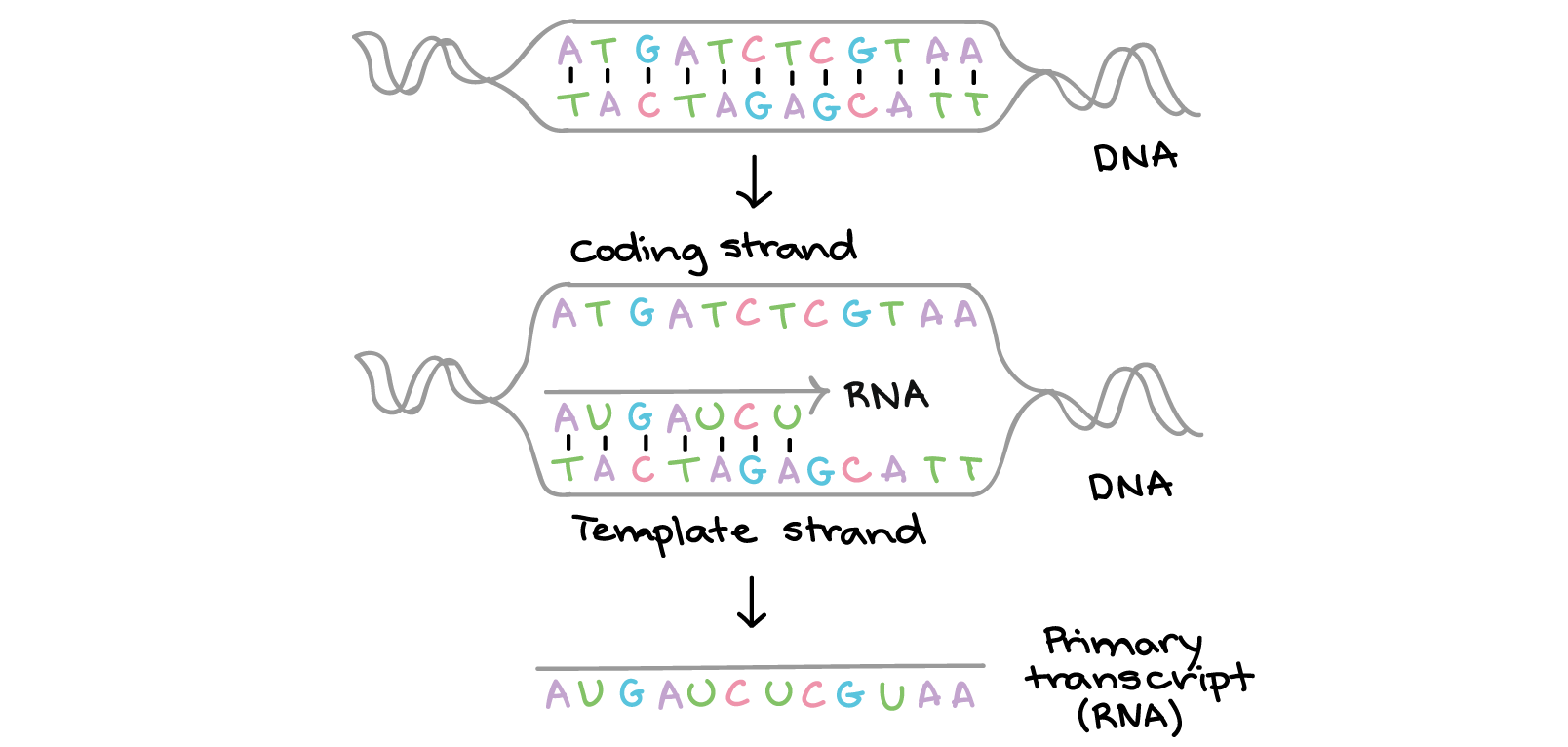
Intro To Gene Expression Central Dogma Article Khan Academy

Dna Transcription Learn Science At Scitable

6 Questions About Dna Answered Britannica
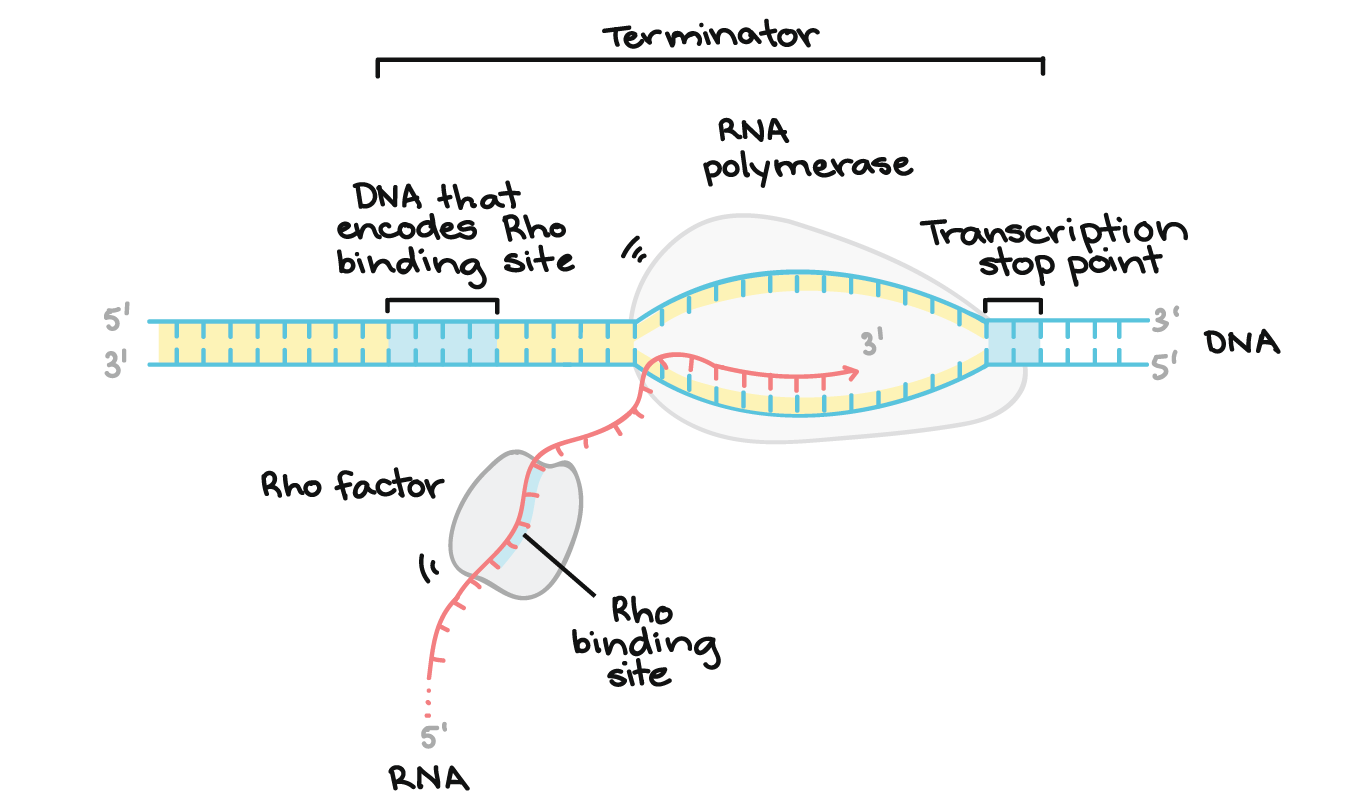
Stages Of Transcription Initiation Elongation Termination Article Khan Academy
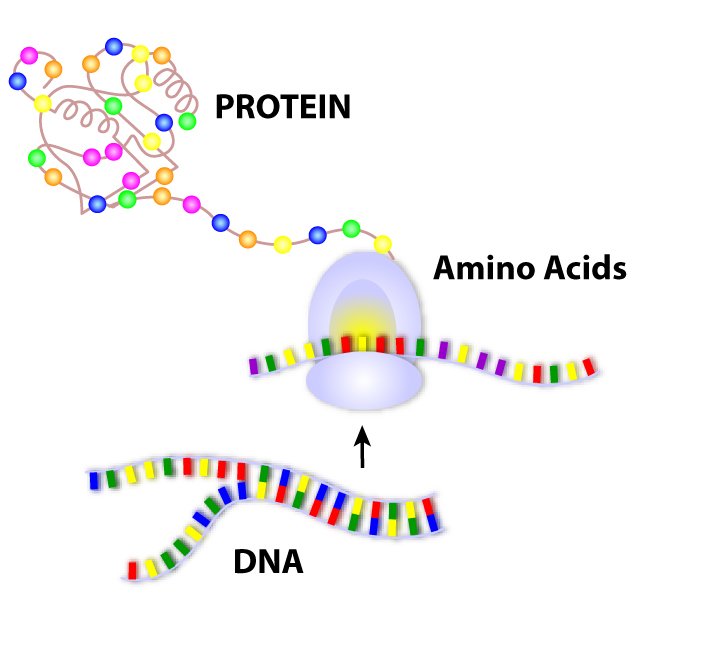
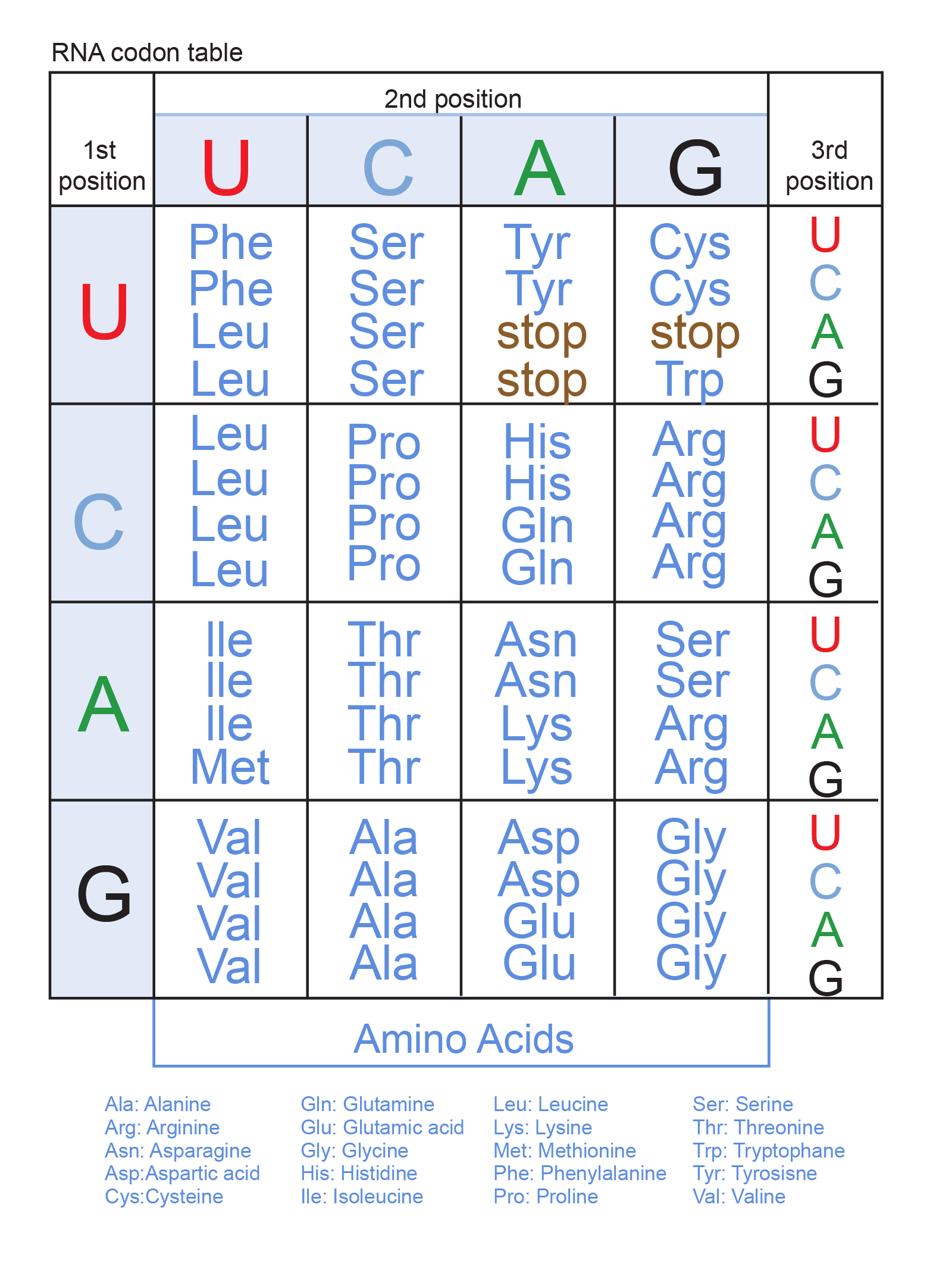

Comments
Post a Comment